What is a Thyroid Disorder?
Thyroid disorders refer to various conditions that impact the thyroid gland, one of the endocrine glands responsible for producing hormones to regulate bodily functions such as metabolism, heart rate, sweating, and energy consumption. Along with the pituitary, adrenal, and parathyroid glands, as well as specialized cells within the pancreas, the thyroid gland plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s balance.
Patients who have a family history of thyroid cancer or who underwent radiation therapy to their head or neck during childhood for reasons like acne or adenoids are at a higher risk of developing thyroid malignancy.
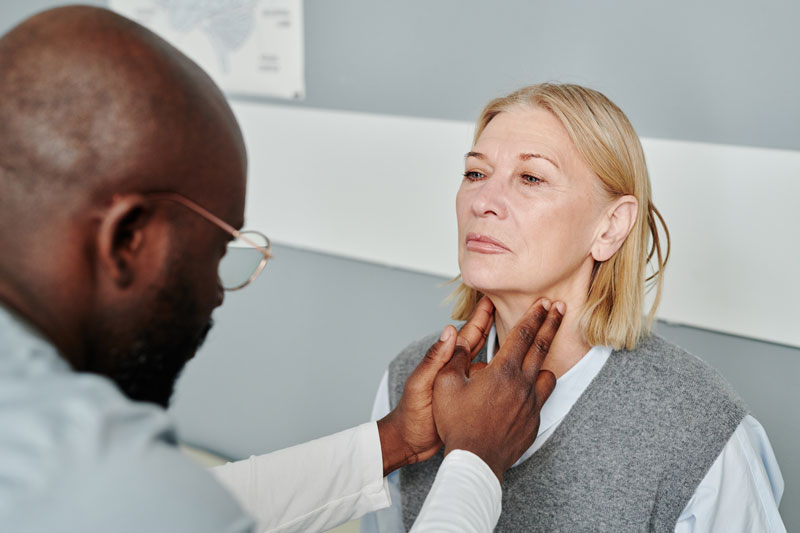
How Are Thyroid Disorders Diagnosed?
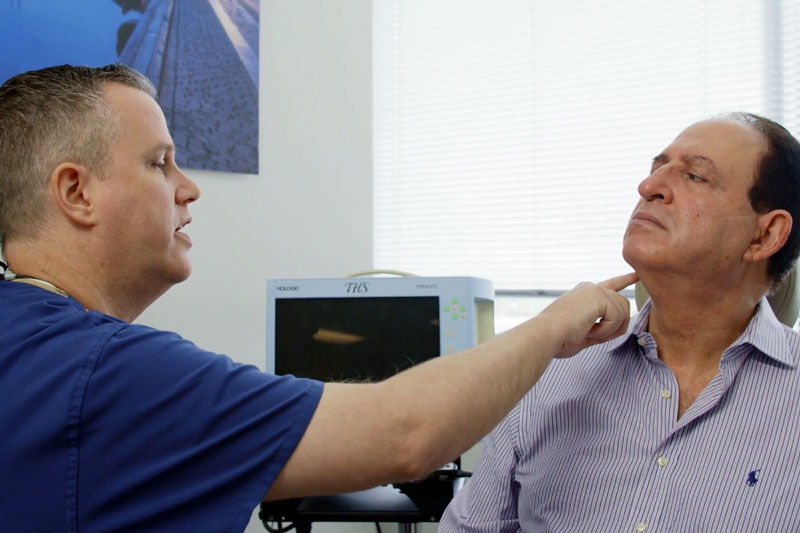
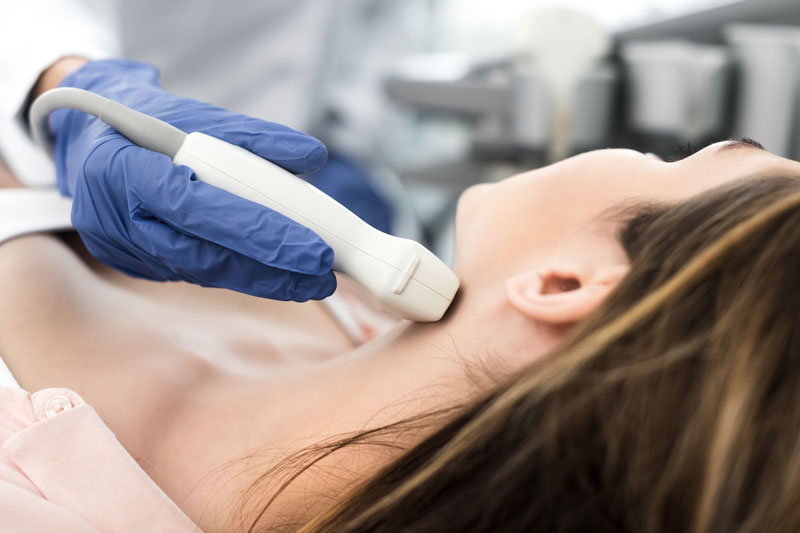
To determine whether there is an abnormality in thyroid function or the presence of a thyroid mass, a medical history and physical examination are conducted by your doctor. Additional evaluations such as blood tests, imaging studies, or fine-needle aspiration may be necessary. During the physical examination, the doctor will inspect the neck area and ask you to lift your chin to highlight the thyroid gland’s visibility. The tests that the doctor may order include:
- An ultrasound examination of your neck and thyroid
- Blood tests of thyroid function
- Evaluation of the larynx/vocal cords with a mirror or fiberoptic telescope
- A radioactive thyroid scan
- A fine-needle aspiration biopsy
- A chest X-ray
- A CT scan or MRI scan
Thyroid Surgery
When thyroid cancer is detected or suspected, or a benign thyroid nodule becomes too large, causing difficulties in swallowing or breathing, surgery may be required. In some instances, when hyperthyroidism doesn’t respond to medical or radioactive iodine treatment, surgery may also be recommended.
The surgical procedure for removing the thyroid gland is called a thyroidectomy, which can be either a total thyroidectomy to remove the entire gland or a thyroid lobectomy to remove half of it.
Following a total thyroidectomy, lifelong hormone replacement therapy is necessary.

Parathyroid (Hyperparathyroidism)

What Causes a Parathyroid Disorder?
When the parathyroid glands produce excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH), various issues can arise.
- Hypercalcemia occurs when the blood calcium level rises, causing the body to absorb excessive calcium from food, leading to calcium loss from bones (osteoporosis). Hypercalciuria, or high levels of calcium in urine, can also result in kidney stones.
- An adenoma, a noncancerous tumor, usually develops in the overactive parathyroid gland responsible for PTH overproduction. It is worth noting that hyperparathyroidism is only rarely linked to cancer.
- PTH also causes a reduction in blood phosphorus levels by increasing the excretion of phosphorus in the urine.
Parathyroid Surgery
Deciding whether to proceed with parathyroid surgery hinges on a number of factors, such as the severity of symptoms and the amount of calcium present in the bloodstream. Once diagnosed, imaging tests are usually conducted to identify the problem’s source.
Surgery is performed under general anesthesia, and patients can often be discharged on the same day.
As with any surgery, there are inherent risks, including bleeding, infection, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Parathyroid surgery may result in damage to the thyroid gland or vocal cords, as well as breathing difficulties. Moreover, the patient may be at risk of developing hypocalcemia, a condition characterized by low calcium levels, but this can be easily remedied.