How do I Know if I Need Hearing Aids?
Recognizing the signs of hearing loss is crucial for maintaining your quality of life. Hearing aids can significantly improve your ability to communicate and engage with the world around you. Common signs you should speak to your provider at The ENT & Allergy Centers of Texas about your hearing concerns include but aren’t limited to:
- Difficulty hearing conversations
- Turning up the volume on the television, your phone, and other devices
- Tinnitus or ringing in the ears
- Withdrawing from social events due to difficulty hearing conversations
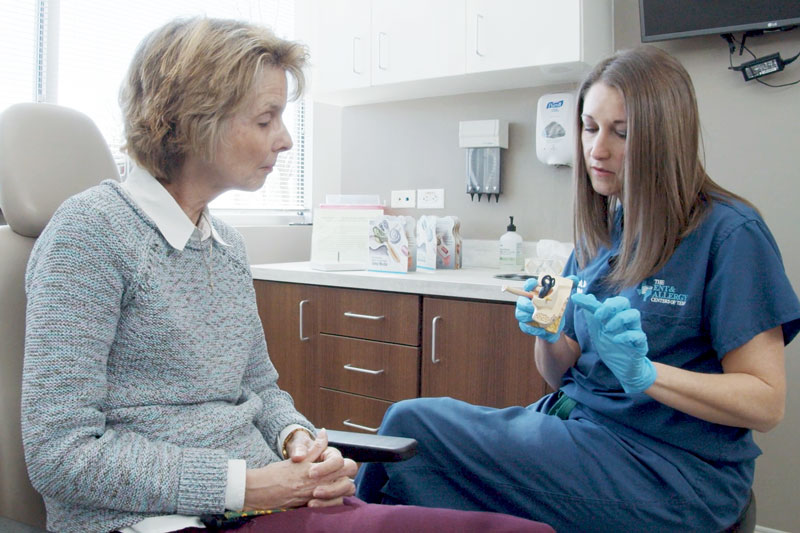
If you notice any of the signs mentioned above, it’s essential to consult an audiologist. Audiologists specialize in hearing health. They conduct tests to identify the nature and extent of your hearing loss, allowing for personalized device programming. Audiologists also address tinnitus and provide customized solutions for this condition. Working with an audiologist ensures you receive personalized care and optimal device settings, easing the adjustment process.
How Do Hearing Aids Work?
Hearing aids capture sounds through a tiny microphone, converting them into digital or electronic signals. These signals are amplified and customized to meet the wearer’s unique needs. Despite variations in form and fit, most hearing aids operate on this basic principle.
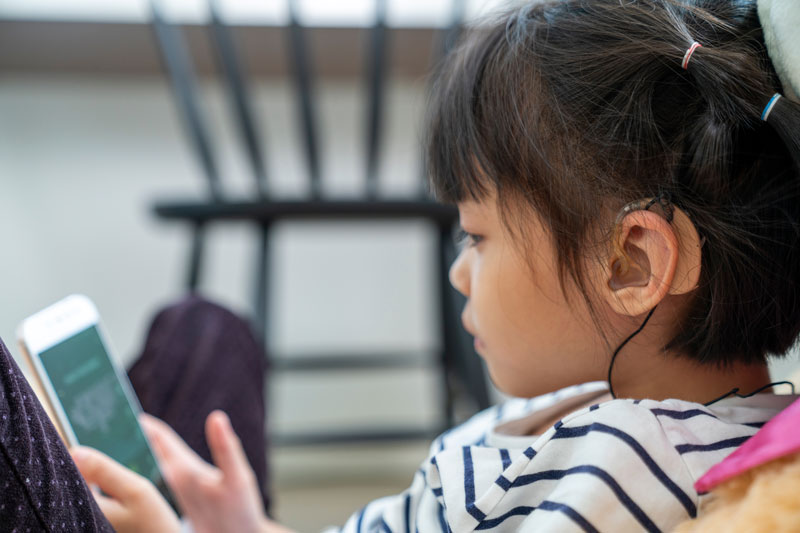

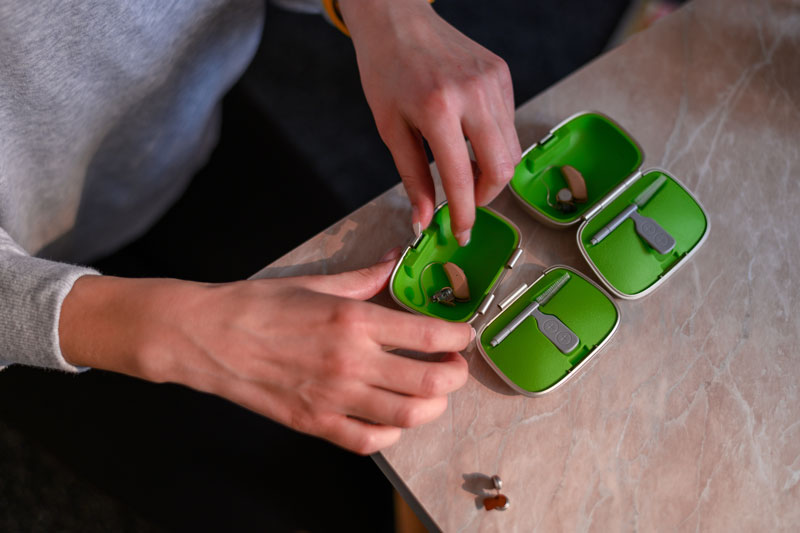
How do I Know What Kind of Hearing Aid I’ll Need?
Hearing aids come in various styles, each with unique benefits:
In-the-Ear (ITE): Custom-fitted to the outer ear, ITE aids are more extensive but more discreet than Behind-the-Ear (BTE) aids. They are easier to handle and may include features like directional microphones.
Behind-the-Ear (BTE): BTE aids are ideal for profound hearing loss, offering higher power and advanced features. They are also available in various colors to blend with skin and hair tones.
In-the-Canal (ITC) and Completely-in-the-Canal (CIC): These aids fit snugly inside the ear canal, making them less visible but potentially more complicated to handle and requiring frequent cleaning.
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC): With a tiny speaker inside the ear canal and the main body behind the ear, RIC aids provide a comfortable fit and natural sound quality.
Pediatric: Typically, BTE aids are reliable for developing language skills and providing consistent, understandable sounds for children.
Selecting the right hearing aid involves several considerations, including the type of hearing loss you’re experiencing, how severe it is, and what lifestyle, budget, and size best suit your needs.
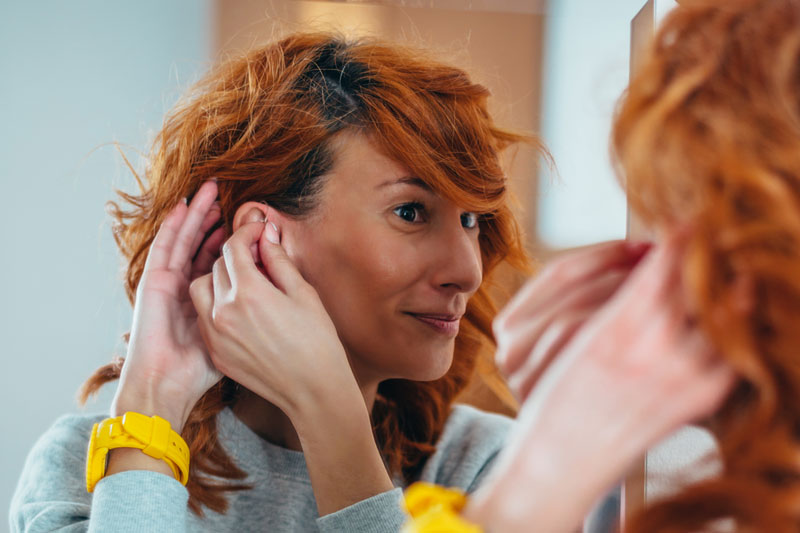

What Are the Benefits of Hearing Aids?
Hearing aids offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved ability to engage in conversations with loved ones and colleagues.
- Enhanced relationships due to better communication.
- Increased confidence in social and professional situations.
- Better self-esteem and productivity.
- More energy, independence, and security.
It takes time to adjust to hearing aids. At first, amplified sounds, including your voice, may seem very strong. Using them consistently is essential; after a few weeks, you will become more accustomed to the sounds of voices and your surroundings. It may take several months to adjust fully. Hearing aids usually last 3 to 7 years, depending on the type of device and how well they are maintained. Proper care can help extend their lifespan.
Hearing Loss Specialist in Northern Texas
If you are experiencing hearing loss, contact The ENT & Allergy Centers of Texas to schedule a consultation. Our audiologists are trained in the latest hearing aid technologies and are dedicated to providing the best fit and function for your lifestyle needs. Call a location near you to take the first step towards better hearing and an improved quality of life.